The Japanese currency is “Yen (円)“. Yen symbol is “¥“.
In this guide, we will cover everything from the basics of the yen to the new bills you’ll be using.
Understanding Japanese Currency “Yen” – Coins and Bills
The yen comes in both coins and banknotes (paper currency / bills) – hereinafter ‘bill (s)’.
The coins are available in 6 denominations.

The bills are available in 4 denominations.
In addition to the 1,000 yen, 5,000 yen, and 10,000 yen bills, Japan also has 2,000 yen bills. However, they are not widely circulated and are rarely seen.

Japan’s New Banknotes in 2024: What Travelers Need to Know
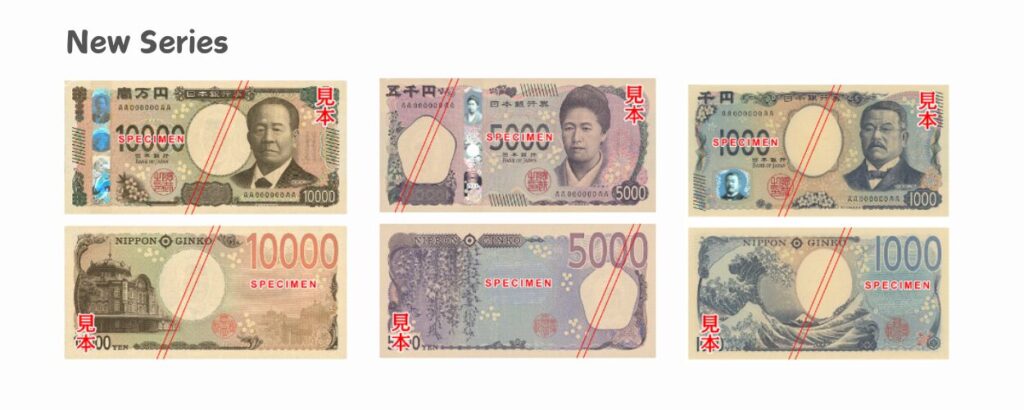

In July 2024, Japan introduced a new series of bills, marking the first significant update in two decades. The new bills feature enhanced security features, including holograms and microprinting, to combat counterfeiting.
Will Old Machines Accept New Bills?

You might see signs like above on vending machines but what does it mean?
Despite the release of the new bills in 2024, not all machines in Japan are equipped to accept them immediately. This can include vending machines, ticket machines at train stations, and even some ATMs. Travelers should be aware that older machines might still only accept the previous versions of the yen. While major establishments will likely update their machines promptly.
Update: January 2026
These signs are becoming much less common, and most machines travelers encounter are now updated to accept the new bills.
When You Still Need Cash in Japan
Japan is becoming more cashless each year, but there are still situations where cash is the easiest—or sometimes the only—option, especially when traveling.
You may need cash for:
- Small local restaurants or family-run shops
- Food stalls and traditional markets
- Ticket machines in rural areas
- Coin lockers and parking machines
- Temple and shrine entrance fees (admission fees)
- Offerings, amulets, and goshuin (temple and shrine stamps)
In particular, temples and shrines often require cash. Admission fees are usually paid in cash, and having coins ready for offerings or goshuin makes the experience much smoother. If you plan to visit historical sites or collect goshuin, carrying some small bills and coins is highly recommended.
A Coin Case I Recommend: The Traditional Japanese “Gamaguchi”

To manage coins and small bills while traveling in Japan, I highly recommend using a Japanese “gamaguchi” coin purse.
A gamaguchi is a traditional clasp-style wallet that opens wide, making it very easy to see and access your coins.
Why a Gamaguchi Works Well in Japan
- Easy access to coins for temples, vending machines, and ticket machines
- Opens wide, so you don’t need to dig around
- Compact and lightweight
- Very Japanese in style — great as a souvenir, too
👉 You can browse popular options here:
Japanese Gamaguchi Coin Purses on Amazon Japan
(When searching, try the keyword: がま口財布 小銭入れ)
Currency Exchange and Where to Exchange Money in Japan
When it comes to getting yen in Japan, there are several options available. Currency exchange services are found at international airports, major banks, and hotels, offering convenient access to yen.
It’s a good idea to have some yen on hand before you arrive in Japan for immediate expenses like transportation or snacks.

Most major airports in Japan, such as Narita, Haneda, and Kansai International Airports, offer currency exchange services. These exchange counters are usually located in the arrival halls and operate from early morning until late evening. While convenient, airport exchange rates may not always be the best, so it’s worth comparing rates if you have time.
Banks in Japan provide reliable currency exchange services. Banks like Mitsubishi UFJ, Sumitomo Mitsui, and Mizuho have branches throughout Japan. They usually offer better rates compared to airports and hotels. However, banks may have limited operating hours, typically from 9 AM to 3 PM on weekdays. You may need to show your passport.
Many larger hotels in Japan offer currency exchange services at the front desk. While convenient, the exchange rates might not be as favorable as those at banks or specialized exchange counters. It’s a good option if you need a small amount of cash quickly.

Automated currency exchange machines are becoming more common in Japan, especially in busy areas like airports, train stations, and shopping centers. They offer competitive rates and are available 24/7, making them a convenient option.
What is a Payment Tray? A Unique and Convenient Tradition
If you are traveling Japan or have recently arrived, you might notice a small but significant detail when making a purchase: the Payment Tray.

This little tray, often placed near the cashier, is where you place your cash or credit card when paying for goods or services.
When you are ready to pay, place your cash or credit card on the tray provided.
The cashier will take your payment from the tray, process the transaction, and place any change or receipts back on the tray for you to collect.
Once the cashier has placed your change or receipt on the tray, you can then take it.
Why is it convenient?
- Hygiene:
The payment tray helps minimize direct contact between customers and cashiers, promoting better hygiene. - Organization:
It helps keep the payment process organized, especially if you are paying with many coins. - Respect and Efficiency:
This method is part of Japan’s culture of respect and politeness. It ensures that the transaction is smooth and efficient, making the transaction feel more formal and courteous.
All About Japanese Yen
This article covered everything you need to know about the Japanese Yen, from understanding the coins, newly updated bills, currency exchange in Japan, and Japan’s cash-based culture.
- Have some yen on hand before you arrive in Japan for immediate expenses.
- Check the money exchange options.
- A coin purse will come in handy in Japan.

